Learning is facilitated when graphics and texts work together to communicate the instructional message (Clark & Mayer, 2016). Graphics are robust materials to promote learning. They are also called as “pictorial expression of information”. Winn (1989) asserts “graphics convey meaning by making the complex more simple and the abstract more concrete”.However, it is important to use graphics for instructional purposes. Woodward (1999) state that many of the graphics embedded in textbooks do not serve educational purposes. Educators should be aware of how to exploit graphics to enhance learning and teaching.
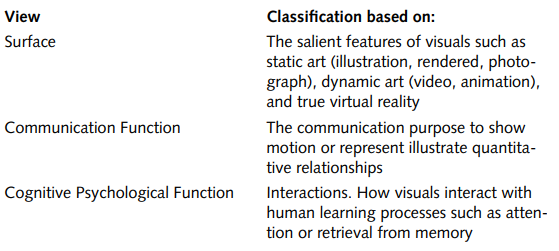
Clark and Lyons (2004) present three different views of visuals based on their
(1) surface features that focus on what they look like and how they are created
(2) communication functions that focus on how they convey information, and
(3) psychological functions that focus on how they facilitate human learning processes.
Communication Functions of Graphics
1. Representational visuals to demonstrate content in a concrete manner

2. Decorative visuals to attract people and serve athestic purposes.

It is important to keep in mind that decorative visuals have the least instructional value. In addition, it may cause extraneous load and distract readers. See here for detailed analysis.
3. Organizational visuals to illustrate qualitative relationships.
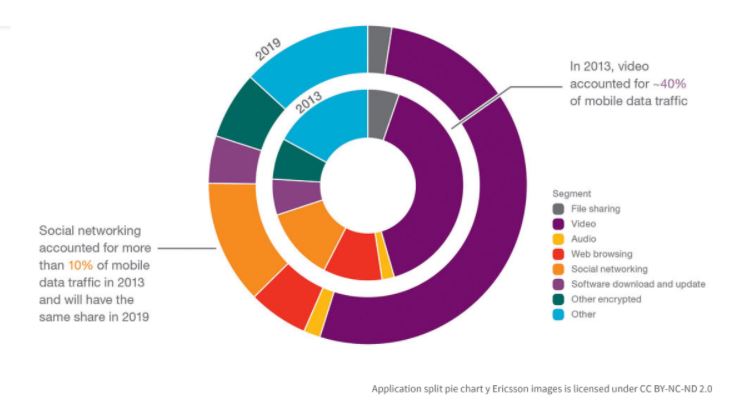
4. Relational visuals to depict quantitative relationships
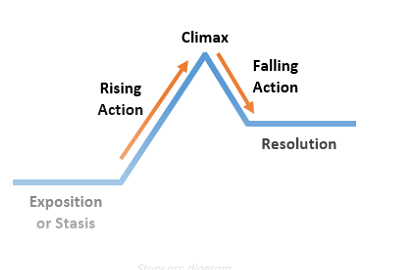
5. Transformational visuals to illustrate changes over time, movements or stages.
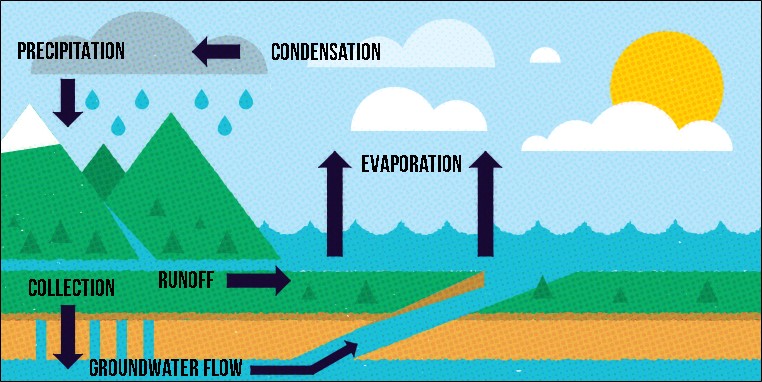
6. Interpretive visuals to depict abstract concepts
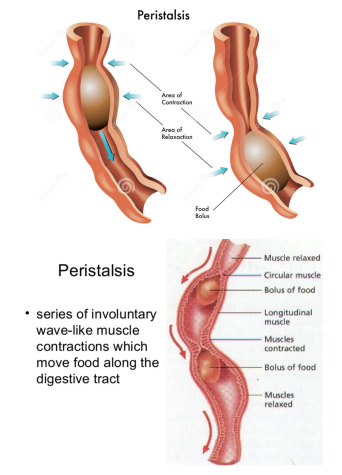
7. Mnemonic visuals to help learners recall relevant information
Psychological Functions of Graphics
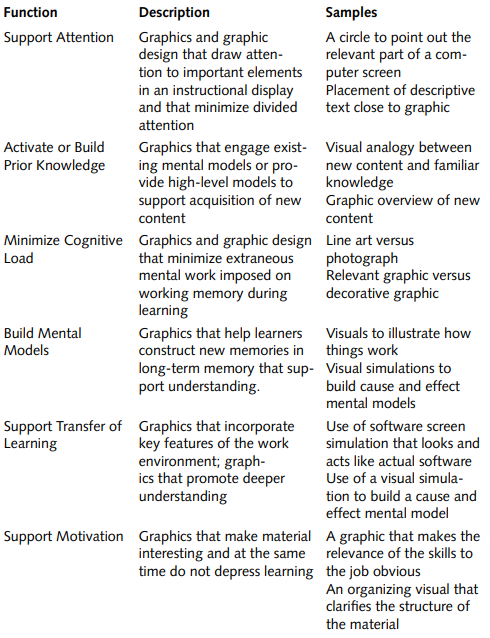
*Tables are retrieved from the book, Graphics for learning (Clark & Lyons, 2004)
Hopefully, this blog provides brief information to understand and plan the graphical elements for instructional purposes. If you are looking for more information about creating and designing graphich, this website here will help you gain in-depth information.
Please feel free to contact me if you need any further information.
References
Clark, R. C., & Mayer, R. E. (2016). E-learning and the science of instruction: Proven guidelines for consumers and designers of multimedia learning. John Wiley & Sons.
Clark, R. C., & Lyons, C. (2004). Graphics for learning: Proven guidelines for planning. Designing, and Evaluating Visuals in Training Materials, Pfeiffer.
Winn, W. (1989). 7 The Design and Use of Instructional Graphics. Advances in Psychology, 125–144.